Burgess fleet gets a face lift!
27 Nov 2024
The Burgess Diagnostics mobile fleet has a fresh new look thanks to the team at Sign UK Limited. Read more
The term “dysplasia” means abnormal development of a tissue or organ. Elbow dysplasia therefore means that there has been abnormal development of the elbow joint. Elbow dysplasia, is really an umbrella term for a number of different conditions of this joint.
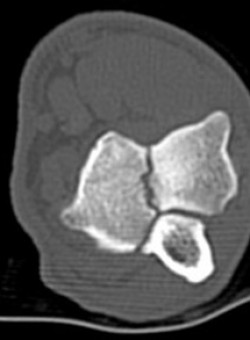
Typically affected dogs show lameness of one or both front legs, stiffness, especially after lying down and reluctance to exercise. In most cases, orthopaedic examination reveals elbow swelling and pain, with a restricted range of movement as the joint becomes thickened. In a small number of dogs the elbows are painful but not swollen and the diagnosis in these cases can be challenging. To aid diagnosis, a Computerised Tomography (CT) Scanner can be used, which scans the entire elbow in about 6 seconds, acquiring images that are just 0.625mm thick allowing the anatomy to be viewed in great detail.
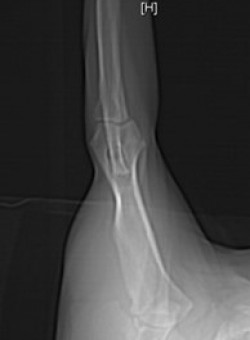
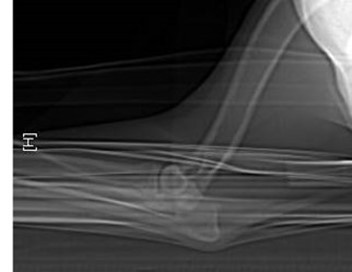
A developmental defect within the elbow joint, where a small crack or fissure separates the coronoid process from the rest of the ulna, it most commonly occurs on the inner or medial process, this separation often causes pain and joint instability.
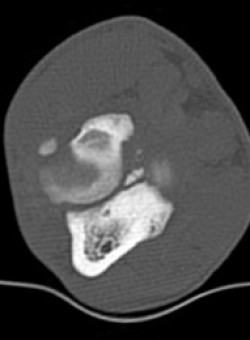
UAP often occurs in young large breed dogs such as German Shepherd, and is a condition in which a bony protuberance within the elbow becomes detached from the ulna bone, causing pain and lameness.
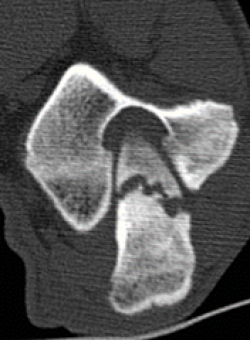
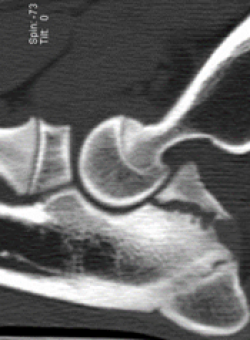
IOHC creates a weak area within the humeral bone predisposing the area for development of condylar fractures. While IOHC is not actually a fracture itself (since it never fused to begin with), IOHC is a defect and may lead to a fracture of the condyle in the future.
27 Nov 2024
The Burgess Diagnostics mobile fleet has a fresh new look thanks to the team at Sign UK Limited. Read more
3 Sep 2024
We are delighted to announce that the Burgess Diagnostics Mobile CT service will now be visiting Rase Veterinary Centre in Lincolnshire, once every four weeks. Read more