Which modality should you choose - MRI or CT?
When a patient requires cross-sectional imaging for evaluation of a particular body part, a veterinary team have a choice between Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). The easy reference table below details the capabilities of each modality when considering specific anatomic regions. Please note this is a representation of the capabilities of each modality and is not an exhaustive list.
Download the Which Modality - Reference Guide
If you would like to discuss a case before imaging, for advice on modality selection, please do not hesitate to contact us by email at clinicalservices@burgessdiagnostics.com
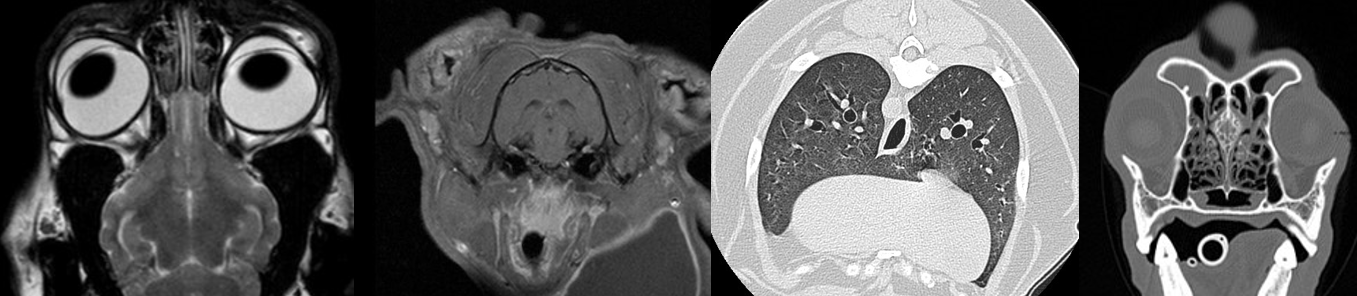
| Region |
| Central Nervous System (CNS) |
| MRI |
|
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE: BRAIN
- Intracranial Disease
- Intracranial Vascular Disease
- Meningitis
- Encephalitis
- Haemorrhage
- Oedema
- Epilepsy
- Hydrocephalus
- Metastasis
- Cranial Nerve Disease
- Degenerative Brain Disease
- Foramen Magnum Herniation
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE: SPINE
- Intervertebral Disc Disease
- Degenerative Myelopathy
- Meningitis
- Diskospondylitis
- Haemorrhage
- FCE (Fibrocartilaginous Emboli)
- Syringomyelia
- Neoplasia
- Arachnoid Cysts
- Wobbler Syndrome
- Lumbar Sacral Disease
- Trauma to the Spine
- Atlanto-occipital Subluxation
|
| CT |
|
BRAIN
- Hydrocephalus
- Contrast Enhancing Lesions
SPINE
- CT Myelography can be used to identify significant sites of spinal cord compression
- Vertebral Body Trauma
- Vertebral Body Neoplasia
|
| Nasal cavities, sinuses, oral, optic |
| MRI |
|
- Neoplasia
- Osteomyelitis
- Aspergillosis
- Palatine Destruction
- Masticatory Myositis
- Foreign Body
|
| CT |
|
- Neoplasia
- Osteomyelitis
- Aspergillosis
- Palatine Destruction
- Foreign Body
- Dental Imaging
- CT Guided Biopsies
|
| External, middle and inner ears |
| MRI |
|
- Tympanic Bulla Wall Erosion
- Neoplasia
- Lymphadenopathy
- Cranial Nerves VII VIII
- Semi-circular Canals
|
| CT |
|
- Tympanic Bulla Wall Erosion
- Neoplasia
- Lymphadenopathy
- Semi-circular Canals
|
| Thorax |
| MRI |
|
- Mediastinal Mass
- Thoracic Wall Mass
|
| CT |
|
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE
- Neoplasia
- Metastasis
- Pneumothorax
- Foreign Body
- Abscess
- CT Guided Biopsy
|
| Abdomen & Pelvic Region |
| MRI |
|
- Neoplasia
- Prostate
- Hips
- Ilio-psoas Injury
- Adrenals
- Cysts
|
| CT |
|
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE
- Neoplasia
- Bladder
- Ectopic Ureters
- IVU (Intravenous Urography)
- Portosystemic Shunts
- Renal Cysts
- Abscess
- Lymphadenopathy
- Liver Pathology
|
| Extremity joints |
| MRI |
|
- Medial Shoulder Injury
- Bone Enema
- Osteochondritis
- Arthrograms
- Muscular Injuries
- Elbow Dysplasia
- Cruciate Ligaments
- Meniscal Injury
- Cartilage Pathology
- Neoplasia
- Foreign Body
|
| CT |
|
- Multiple joints in one session
- Angular Limb Deformity
- Scans for 3D printing for fracture repair planning
- Elbow Dysplasia
- Neoplasia
- Osseous Disease
- Foreign Body
|
| Patients with metallic implants |
| MRI |
|
Although most implants are non-ferrous and safe for MRI, they must be discussed with Burgess Diagnostics.
Implants inserted within the area of interest may cause artefacts and provide non-diagnostic studies. |
| CT |
|
Implants inserted within the area of interest may cause artefacts and provide non-diagnostic studies. |
| Region |
| Central Nervous System (CNS) |
| MRI |
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE: BRAIN
- Intracranial Disease
- Intracranial Vascular Disease
- Meningitis
- Encephalitis
- Haemorrhage
- Oedema
- Epilepsy
- Hydrocephalus
- Metastasis
- Cranial Nerve Disease
- Degenerative Brain Disease
- Foramen Magnum Herniation
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE: SPINE
- Intervertebral Disc Disease
- Degenerative Myelopathy
- Meningitis
- Diskospondylitis
- Haemorrhage
- FCE (Fibrocartilaginous Emboli)
- Syringomyelia
- Neoplasia
- Arachnoid Cysts
- Wobbler Syndrome
- Lumbar Sacral Disease
- Trauma to the Spine
- Atlanto-occipital Subluxation
|
| CT |
BRAIN
- Hydrocephalus
- Contrast Enhancing Lesions
SPINE
- CT Myelography can be used to identify significant sites of spinal cord compression
- Vertebral Body Trauma
- Vertebral Body Neoplasia
|
| Nasal cavities, sinuses, oral, optic |
| MRI |
- Neoplasia
- Osteomyelitis
- Aspergillosis
- Palatine Destruction
- Masticatory Myositis
- Foreign Body
|
| CT |
- Neoplasia
- Osteomyelitis
- Aspergillosis
- Palatine Destruction
- Foreign Body
- Dental Imaging
- CT Guided Biopsies
|
| External, middle and inner ears |
| MRI |
- Tympanic Bulla Wall Erosion
- Neoplasia
- Lymphadenopathy
- Cranial Nerves VII VIII
- Semi-circular Canals
|
| CT |
- Tympanic Bulla Wall Erosion
- Neoplasia
- Lymphadenopathy
- Semi-circular Canals
|
| Thorax |
| MRI |
- Mediastinal Mass
- Thoracic Wall Mass
|
| CT |
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE
- Neoplasia
- Metastasis
- Pneumothorax
- Foreign Body
- Abscess
- CT Guided Biopsy
|
| Abdomen & Pelvic Region |
| MRI |
- Neoplasia
- Prostate
- Hips
- Ilio-psoas Injury
- Adrenals
- Cysts
|
| CT |
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE
- Neoplasia
- Bladder
- Ectopic Ureters
- IVU (Intravenous Urography)
- Portosystemic Shunts
- Renal Cysts
- Abscess
- Lymphadenopathy
- Liver Pathology
|
| Extremity joints |
| MRI |
- Medial Shoulder Injury
- Bone Enema
- Osteochondritis
- Arthrograms
- Muscular Injuries
- Elbow Dysplasia
- Cruciate Ligaments
- Meniscal Injury
- Cartilage Pathology
- Neoplasia
- Foreign Body
|
| CT |
- Multiple joints in one session
- Angular Limb Deformity
- Scans for 3D printing for fracture repair planning
- Elbow Dysplasia
- Neoplasia
- Osseous Disease
- Foreign Body
|
| Patients with metallic implants |
| MRI |
Although most implants are non-ferrous and safe for MRI, they must be discussed with Burgess Diagnostics.
Implants inserted within the area of interest may cause artefacts and provide non-diagnostic studies. |
| CT |
Implants inserted within the area of interest may cause artefacts and provide non-diagnostic studies. |
| Region |
| Central Nervous System (CNS) |
| MRI |
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE: BRAIN
- Intracranial Disease
- Intracranial Vascular Disease
- Meningitis
- Encephalitis
- Haemorrhage
- Oedema
- Epilepsy
- Hydrocephalus
- Metastasis
- Cranial Nerve Disease
- Degenerative Brain Disease
- Foramen Magnum Herniation
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE: SPINE
- Intervertebral Disc Disease
- Degenerative Myelopathy
- Meningitis
- Diskospondylitis
- Haemorrhage
- FCE (Fibrocartilaginous Emboli)
- Syringomyelia
- Neoplasia
- Arachnoid Cysts
- Wobbler Syndrome
- Lumbar Sacral Disease
- Trauma to the Spine
- Atlanto-occipital Subluxation
|
| CT |
BRAIN
- Hydrocephalus
- Contrast Enhancing Lesions
SPINE
- CT Myelography can be used to identify significant sites of spinal cord compression
- Vertebral Body Trauma
- Vertebral Body Neoplasia
|
| Nasal cavities, sinuses, oral, optic |
| MRI |
- Neoplasia
- Osteomyelitis
- Aspergillosis
- Palatine Destruction
- Masticatory Myositis
- Foreign Body
|
| CT |
- Neoplasia
- Osteomyelitis
- Aspergillosis
- Palatine Destruction
- Foreign Body
- Dental Imaging
- CT Guided Biopsies
|
| External, middle and inner ears |
| MRI |
- Tympanic Bulla Wall Erosion
- Neoplasia
- Lymphadenopathy
- Cranial Nerves VII VIII
- Semi-circular Canals
|
| CT |
- Tympanic Bulla Wall Erosion
- Neoplasia
- Lymphadenopathy
- Semi-circular Canals
|
| Thorax |
| MRI |
- Mediastinal Mass
- Thoracic Wall Mass
|
| CT |
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE
- Neoplasia
- Metastasis
- Pneumothorax
- Foreign Body
- Abscess
- CT Guided Biopsy
|
| Abdomen & Pelvic Region |
| MRI |
- Neoplasia
- Prostate
- Hips
- Ilio-psoas Injury
- Adrenals
- Cysts
|
| CT |
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE
- Neoplasia
- Bladder
- Ectopic Ureters
- IVU (Intravenous Urography)
- Portosystemic Shunts
- Renal Cysts
- Abscess
- Lymphadenopathy
- Liver Pathology
|
| Extremity joints |
| MRI |
- Medial Shoulder Injury
- Bone Enema
- Osteochondritis
- Arthrograms
- Muscular Injuries
- Elbow Dysplasia
- Cruciate Ligaments
- Meniscal Injury
- Cartilage Pathology
- Neoplasia
- Foreign Body
|
| CT |
- Multiple joints in one session
- Angular Limb Deformity
- Scans for 3D printing for fracture repair planning
- Elbow Dysplasia
- Neoplasia
- Osseous Disease
- Foreign Body
|
| Patients with metallic implants |
| MRI |
Although most implants are non-ferrous and safe for MRI, they must be discussed with Burgess Diagnostics.
Implants inserted within the area of interest may cause artefacts and provide non-diagnostic studies. |
| CT |
Implants inserted within the area of interest may cause artefacts and provide non-diagnostic studies. |
| Region |
MRI |
CT |
| Central Nervous System (CNS) |
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE: BRAIN
- Intracranial Disease
- Intracranial Vascular Disease
- Meningitis
- Encephalitis
- Haemorrhage
- Oedema
- Epilepsy
- Hydrocephalus
- Metastasis
- Cranial Nerve Disease
- Degenerative Brain Disease
- Foramen Magnum Herniation
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE: SPINE
- Intervertebral Disc Disease
- Degenerative Myelopathy
- Meningitis
- Diskospondylitis
- Haemorrhage
- FCE (Fibrocartilaginous Emboli)
- Syringomyelia
- Neoplasia
- Arachnoid Cysts
- Wobbler Syndrome
- Lumbar Sacral Disease
- Trauma to the Spine
- Atlanto-occipital Subluxation
|
BRAIN
- Hydrocephalus
- Contrast Enhancing Lesions
SPINE
- CT Myelography can be used to identify significant sites of spinal cord compression
- Vertebral Body Trauma
- Vertebral Body Neoplasia
|
| Nasal cavities, sinuses, oral, optic |
- Neoplasia
- Osteomyelitis
- Aspergillosis
- Palatine Destruction
- Masticatory Myositis
- Foreign Body
|
- Neoplasia
- Osteomyelitis
- Aspergillosis
- Palatine Destruction
- Foreign Body
- Dental Imaging
- CT Guided Biopsies
|
| External, middle and inner ears |
- Tympanic Bulla Wall Erosion
- Neoplasia
- Lymphadenopathy
- Cranial Nerves VII VIII
- Semi-circular Canals
|
- Tympanic Bulla Wall Erosion
- Neoplasia
- Lymphadenopathy
- Semi-circular Canals
|
| Thorax |
- Mediastinal Mass
- Thoracic Wall Mass
|
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE
- Neoplasia
- Metastasis
- Pneumothorax
- Foreign Body
- Abscess
- CT Guided Biopsy
|
| Abdomen & Pelvic Region |
- Neoplasia
- Prostate
- Hips
- Ilio-psoas Injury
- Adrenals
- Cysts
|
IMAGING MODALITY OF CHOICE
- Neoplasia
- Bladder
- Ectopic Ureters
- IVU (Intravenous Urography)
- Portosystemic Shunts
- Renal Cysts
- Abscess
- Lymphadenopathy
- Liver Pathology
|
| Extremity joints |
- Medial Shoulder Injury
- Bone Enema
- Osteochondritis
- Arthrograms
- Muscular Injuries
- Elbow Dysplasia
- Cruciate Ligaments
- Meniscal Injury
- Cartilage Pathology
- Neoplasia
- Foreign Body
|
- Multiple joints in one session
- Angular Limb Deformity
- Scans for 3D printing for fracture repair planning
- Elbow Dysplasia
- Neoplasia
- Osseous Disease
- Foreign Body
|
| Patients with metallic implants |
Although most implants are non-ferrous and safe for MRI, they must be discussed with Burgess Diagnostics.
Implants inserted within the area of interest may cause artefacts and provide non-diagnostic studies. |
Implants inserted within the area of interest may cause artefacts and provide non-diagnostic studies. |
