Scanning a Tiger, a Leopard and a Cheetah at The Big Cat Sanctuary
29 Oct 2025
Our big CAT-scanning day. Find out more about our incredible day at The Big Cat Sanctuary in Kent scanning a tiger, a clouded leopard and a cheetah. Read more
CT is extremely helpful in the evaluation of thoracic disease and is the imaging modality of choice when thoracic radiographs and/or ultrasound are insufficient for diagnosis or when a lesion has been identified, but additional information is required.
CT images provide excellent anatomic and pathologic detail of lung disease and can also be used to assess the pleural space, mediastinum and intrathoracic vasculature. Thoracic CT is quick to perform and often delivers useful results.
A 9-year-old Labrador Retriever was presented for evaluation of a chronic persistent cough which had been present over the past 4 months. The dog remained systemically well and cardiopulmonary auscultation was normal.
Thoracic radiographs were obtained and showed an area of mild unstructured interstitial pattern in the right caudal lung lobe. At this point the decision was made to proceed to CT to further characterise these changes and to determine whether bronchoscopy would be worthwhile.
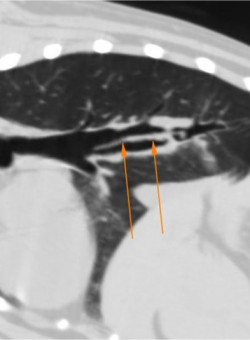
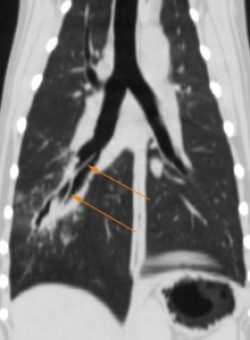
The CT examination showed a dilated right caudal mainstem bronchus with a moderately thickened wall. An irregular, dorsoventrally flattened foreign body was identified within the bronchus, 3.2cm caudal to the tracheal bifurcation.
The dorsal and sagittal reconstructions along the line of the bronchus were used to better define the extent of the foreign material. The distal tip was found to be extending into the next divisional bronchus.
The CT diagnosis was bronchial foreign body with secondary focal bronchopneumonia and reactive mediastinal lymphadenopathy. This was confirmed by bronchoscopy, where the foreign body was identified as a pointed leaf (possibly a Holly leaf), but could not be removed due to concern over possible tearing of the bronchial wall.
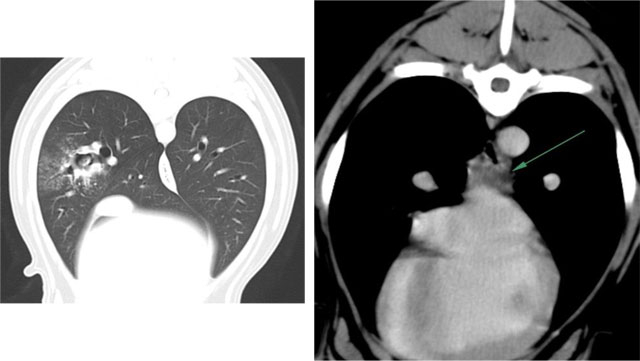
The patient then had a thoracotomy and the CT findings were used to guide extraction of the foreign body, via an incision in the wall of the right caudal mainstem bronchus. CT was useful in this case as neither the clinical presentation, nor the thoracic radiographs were particularly suggestive of a bronchial foreign body. CT provided a fast, definitive diagnosis and enabled precise determination of the extent of the disease. This information is particularly useful when proceeding to bronchoscopy, to ensure that the most distally located foreign material will be completely removed.
Reported by Victoria S Johnson BVSc, DVR, DipECVDI, MRCVS – AVDIS Ltd. Case courtesy of Sophia Tzannes
29 Oct 2025
Our big CAT-scanning day. Find out more about our incredible day at The Big Cat Sanctuary in Kent scanning a tiger, a clouded leopard and a cheetah. Read more
22 Sep 2025
It’s not every day we welcome a gorilla on board one of our mobile CT scanners! Find out more about our amazing day at London Zoo. Read more